Additive Manufacturing for Complex Concrete Casting
Year: 2016-2017
Location: Milan, Italy
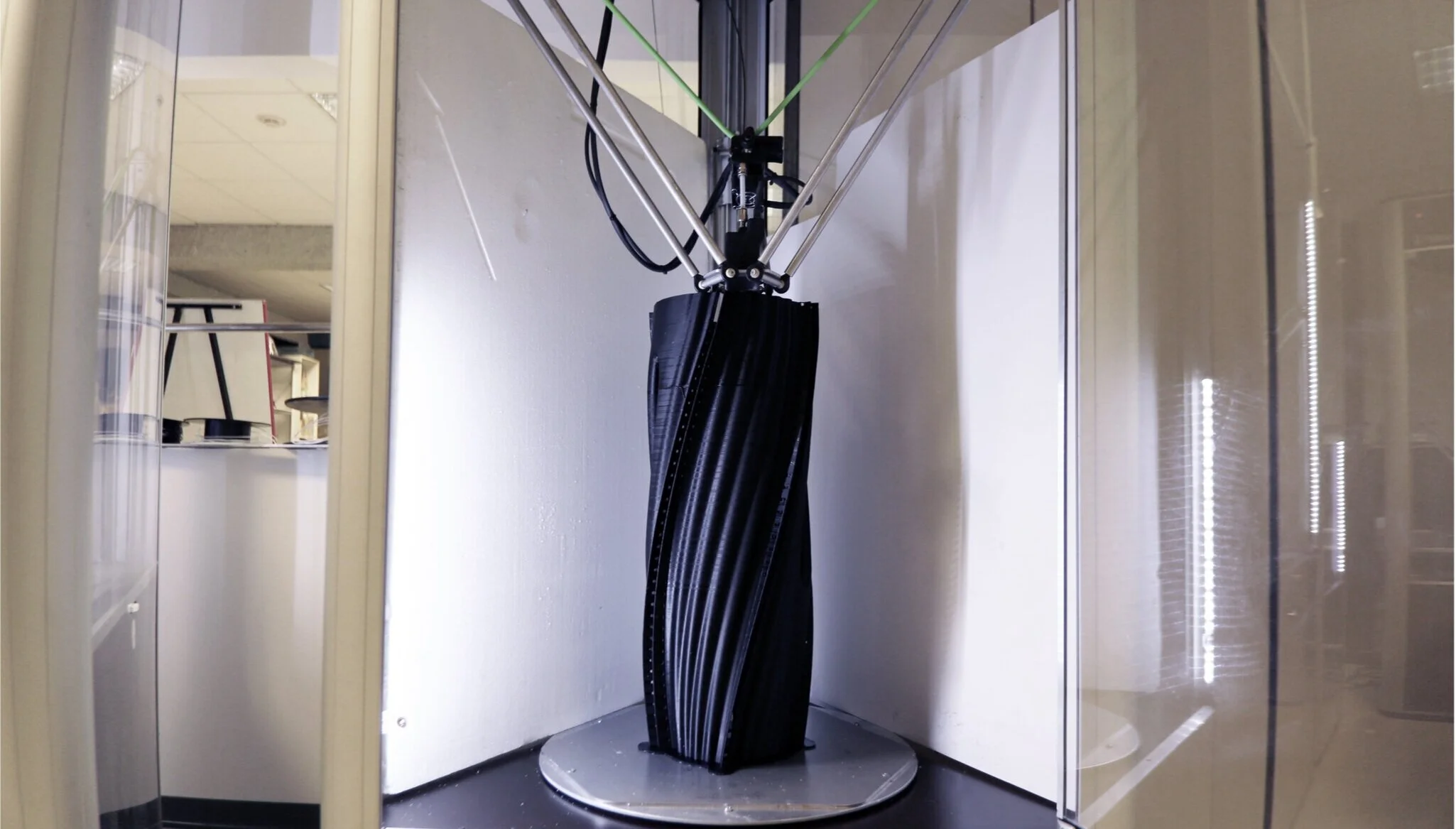
There is a large gap between design possibilities and construction techniques in the field of architecture. Despite more software becoming available to people, construction industry remains as one of the most outdated industries. This thesis was born to create a bridge between these emerging design methods and long-existing casting techniques by introducing a non-traditional casting method. Currently numerous additive manufacturing methods are used to create mass produced formworks. Several studies have been made on the topic but the integration of 3D printing into the realization of complex moulds and the casting of complex customized structures is usually passed over due to the scale issues. The size of the moulds that can be manufactured is limited to the bed size of the possessed printer. This research tackles this issue by generating a connected component system and demonstrates a complex final prototype that proves the easy, cheap manufacturing and assembly. Five major tests were carried out in order to explore the system of concrete casting with 3D printed moulds. The initial tests showed that concrete was too heavy and applying an excessive amount of pressure to the surface of the mould. Therefore the mould needed to be reinforced either by treating the surface with corrugations or adding external reinforcements. The latter experiment investigated the integration of holes for the realization of a form that is very hard to achieve with traditional manufacturing techniques. Since the prototype was in the scale of 1:2 and realized with many but small holes, the attempt of removing the mould was not successful. The last experiment was on the creation of efficient joints to avoid concrete leakage and to provide a continuous surface finishing to the cast block. A system of stitching was developed and applied on the study model. The results were significantly better and more successful. Removing the mould was easy and the fabrication method was enhanced and revealed by the traces of external reinforcements on the cast block.
For further information on the project please contact me!